|
Prague CZ, 2022 Sep 22. BEC tutorial-Living Communications: pmF — pre EMC2022 Prague. |
MiPsociety (2022-09-22) Mitochondr Physiol Network
Abstract: BEC tutorial-Living Communications. Mitochondrial membrane potential and Peter Mitchell’s protonmotive force: elements of the science of bioenergetics. Preceding the EMC 2022 49th European Muscle Conference, Prague, Czech Republic.
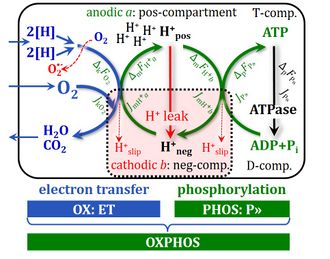
The mitochondrial membrane potential is an element of the science of bioenergetics, linked to the control of respiratory flux and related mitochondrial functions. A PubMed search on ‘mitochondrial membrane potential’ yields 40 000 results and 3452 for 2021 (search 2022-09-20), with a linear increase during the past 20 years. Chapter 8 on ‘Protonmotive pressure and respiratory control’ of Mitochondrial Pathways (Gnaiger 2020) introduces a novel perspective on Peter Mitchell’s protonmotive force, which incorporates the mitochondrial membrane potential. If you find the reading is tough, you are not alone. Join this BEC tutorial-Living Communications for an introduction into the relevant concepts of physical chemistry, which differ from misleading chapters in bioenergetics textbooks on potential gradients, Gibbs energy, protonmotive flow and force, and finally protonmotive pressure. This will introduce students (and teachers) to a new understanding of mitochondrial membrane potential and the protonmotive force, connecting the ideal gas equation, osmotic pressure, the Boltzmann constant and gas constant with Fick’s and Einstein’s diffusion equation. If theory gets tough, join for a follow-up retreat.
• O2k-Network Lab: AT_Innsbruck_Oroboros, CZ Prague Houstek J
Last update: 2022-09-20
This MiPevent is dedicated to Dr. Zdenek Drahota — one of the greatest mitochondrial physiologists of the Czech Republic — at his 90th birthday:
In collaboration with the Mitochondrial Physiology Society - see MiP2017
Venue and local organizers
- Laboratory of Bioenergetics
- Institute of Physiology CAS
- Videnska 1083
- 142 20 Prague 4
- Czech Republic
Zuzana Korandová, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
Tomáš Mráček, RNDr, Head of Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
Pecina Petr, PhD, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
Josef Houstek, Prof, MD, PhD, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
Program
- Blocks of 10 + 5 min comments, questions, discussion
- Sections of Chapter 8, Blue Book
| Time | Section | Topic | a | b | c | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:00-10:15 | 8. | Overview: from Mitchell's four modules to four protonmotive theorems | diffusive pressure gradient | pressure difference and potential difference | diffusive and electric pressure difference | concave to convex flow/force |
| 10:15-10:25 | 8.1. | 1. Vectorial and scalar quantities | amount and charge format | diffusion: gradients and compartments | stoichiometry and advancement | |
| 10:30-10:40 | 8.2. | 2. Why is thermodynamics scary? | chemical potential | metabolic force | Gibbs energy - exergy | |
| 10:45-10:50 | 8.2. | 3. The elementary unit | SI base units | elementary quantities | count on motive units | beyond the Gas constant: Boltzmann, Avogadro, Faraday |
| 11:00-11:10 | 8.3. | 4. Protonmotive force and motive units | Why Δp? | pmF formats | conversion between formats | measurement of the pmF |
| 11:15-11:45 | Coffee/tea - Chat | |||||
| 11:45-11:55 | 8.4.1. | 5. Protonmotive pressure pmP linearity | diffusion gradients and Einstein's diffusion equation | Fick's law | pressure-force confusion | thermodynamics of irreversible processes |
| 12:00-12:10 | 8.4.2. | 6. Compartments: diffusion and osmotic pressure | concave flux/force relation | free activity | infinite forces without explosion | |
| 12:15-12:25 | 8.4.3. | 7. Hydrogen ions and counterions | if the force is in ∆pH | electroneutral exchange of counterions | equilibrium H+ and counterion distribution | concave flow (pressure)/force relation |
| 12:30-12:45 | 8.4.4. | 8. Matrix volume fraction and flux-pressure linearity | anodic volume fraction | closed to open anodic system | from intensity to capacity | non-ohmic proton leak explained by first principles |
| 12:45-13:00 | General discussion with a glass of wine - a taste of Gentle Science |
Lecturer and participants
Erich Gnaiger, PhD., Oroboros Instruments - author of
Participants
- Restricted number of participants: countmax = (29 + 1) x
1. Lukáš Alán, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
2. Zuzana Červinková, Prof, MD, PhD, Lab Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Hradec Kralove, CZ
3. Eva Doleželová, PhD, Institute of Parasitology, Ceske Budejovice, CZ
4. Zdenek Drahota, PhD, Lab of Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
5. Jan Eliáš, MBBCh, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
6. Moustafa Elkalaf, MBBCh, PhD, Lab of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Hradec Kralove, CZ
7. René Endlicher, PhD, Lab of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Hradec Kralove, CZ
8. František Galatík, Laboratory of Physiology, Faculty of Science, Charles University, Prague, CZ
9. Olga Horakova, Laboratory of Adipose Tissue Biology, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, CZ
10. Josef Houstek, Prof, MD, PhD, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
11. Petra Janovska, PhD, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
12. Petr Kašík, Faculty of Science, Charles University, Prague, CZ
13. Michal Knězů, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
14. Eliška Koňaříková, Dr. rer. nat., Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
15. Zuzana Korandová, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
16. Barbora Kudrnovská, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
17. Tomáš Mráček, RNDr, Head of Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
18. Petr Pecina, PhD, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
19. Alena Pecinova, PhD, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
20. Guillermo Puertas Frias, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
21. Maria Jose Saucedo Rodriges, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
22. Ondrej Sobotka, MUDr, PhD, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Hradec Kralove, CZ
23. Pavla Staňková, Mgr, PhD, Lab of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Hradec Kralove, CZ
24. Kateřina Tauchmannová, PhD, Lab Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
25. Lucie Zdrazilova, MSc, First Faculty of Medicine,Charles University, Prague, CZ
26. Petr Zouhar, Institute of Physiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, CZ
Registration and general information
- Informal, no registration fee - send Email to: instruments@oroboros.at
- Limited number of participants
- Provide your name and affiliation (if you wish for the website)
- Provide a foto (if you wish for the website)
COVID-19
- The event will be held in accordance with current COVID regulations. A primary concern must be the safety of our participants and staff, which is why we reserve the right to cancel the event if there are any concerns/restrictions.
Recommended reading
- Mitchell P (1966) Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.09.018
- Gnaiger E (2020) Mitochondrial pathways and respiratory control. An introduction to OXPHOS analysis. 5th ed. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0002 - Chapter 8
- Gnaiger E (2021) The elementary unit — canonical reviewer's comments on: Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (2019) The International System of Units (SI) 9th ed. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:200004.v2
BEC tutorials are listed as MitoGlobal Events.
Labels:
ORO, MiP, 2022, MitoGlobal