Description
ETS substrate types are linked to ETS pathway types in mitochondrial SUIT protocols. These are reduced substrates feeding electrons into the electron transfer system (ETS) at different levels of mitochondrial pathways. Distinction of five mt-pathway types provides the rationale for defining categories of SUIT protocols.
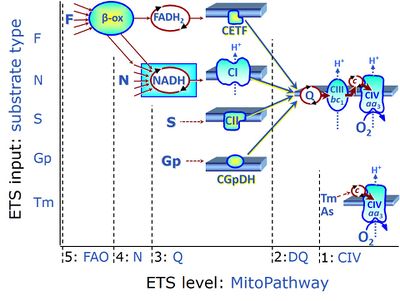
ETS substrates type 1 may be artificial electron donors (e.g. TMPD, Tm) essentially bypassing the ETS, reducing cytochrome c and feeding electrons directly into the terminal electron acceptor, cytochrome c oxidase (CIV) or alternative oxidases (single enzymatic step).
ETS substrates type 2 (Coenzyme Q) feed electrons into Complex III (CIII) with further electron transfer downstream of the Q-junction.
ETS substrates type 3 (NADH, FADH2, succinate, glycerophosphate) feed electrons into respiratory complexes directly upstream of the Q-junction. NADH is the substrate of Complex I (CI). FADH2 is the substrate of electron transferring flavoprotein (CETF) localized on the inner side of the inner mt-membrane. Succinate is the substrate of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH, CII) localized on the inner side of the inner mt-membrane. Glycerophosphate is the substrate of glycerophosphate dehydrogenase complex (CGpDH) localized on the outer face of the inner mt-membrane. Choline is the type 3 substrate of choline dehydrogenase.
ETS pathway type 4 feeds electrons into dehydrogenases and enzyme systems upstream of the type 3 pathway level. Electron transfer from type 4 substrates (N) converges at the N-junction. Representative type N substrates are pyruvate, glutamate and malate, and also citrate, oxoglutarate and others. The corresponding dehydrogenases (PDH, GDH, MDH and mtME; IDH, OgDH) generate NADH, the substrate of Complex I (CI). Fatty acids supporting converging electron transfer to the F-junction might also considered as type 4 substrates. However, the requirement of a combined operation of the F-junction and N-junction puts type F substrates to a higher level of pathway integration.
ETS pathway type 5 feeds electrons into dehydrogenases and enzyme systems upstream of the type 3 pathway level with an obligatory combination of the F-junction and N-junction. Type F substrates are fatty acids involved in β-oxidation, generating (enzyme-bound) FADH2, the substrate of electron transferring flavoprotein (CETF). Succinate does not belong to the type 4 substrates, since FADH2 is the product of CII, whereas FADH2 is the substrate of CETF. Fatty acid oxidation (FAO) not only depends on electron transfer through the F-junction (which is typically rate-limiting) but simultaneously generates NADH and thus depends on N-junction throughput. Hence FAO can be inhibited completely by inhibition of Complex I (CI). In addition and independent of this source of NADH, the type N substrate malate is required as a co-substrate for FAO in mt-preparations, since accumulation of AcetylCoA inhibits FAO in the absence of malate. Malate is oxidized in a reaction catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase to oxaloacetate (yielding NADH), which then stimulates the entry of AcetylCo into the TCA cycle catalyzed by citrate synthase.
Abbreviation: n.a.
Reference: Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
Respiratory state,
SUIT concept
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite
Contributed by Gnaiger E 2016-02-01; edited 2016-02-10, 2016-03-29, 2016-08-20, 2016-09-10
ETS substrate types on different pathway levels
- ETS substrates type 5 on the pathway level of converging FADH2 and NADH-linked dehydrogenases, including beta-oxidation and segments of the TCA cycle:
- F: F-junction substrates, FADH2-linked, fatty acids (FAO)
- ETS substrates type 4 on the pathway level of converging NADH-linked dehydrogenases, including the TCA cycle:
- N: N-junction substrates, NADH-linked (and hence downstream 'CI-linked')
- ETS substrates type 3 on the pathway level of electron transfer complexes converging at the Q-junction:
- Q: Q-junction substrates
- NADH, substrate of CI
- FADH2, substrate of CETF
- S: Succinate, substrate of CII
- Gp: Glycerophosphate, substrate of CGpDH
- Choline: substrate of choline dehydrogenase
- ETS substrates type 1 on the single step level of cytochrome c oxidase (CIV), the terminal step in the aerobic electron transfer system: