Hidalgo-Gutierrez 2021 Antioxidants (Basel): Difference between revisions
m (Gnaiger Erich moved page Hidalgo-Gutiérrez 2021 Antioxidants (Basel) to Hidalgo-Gutierrez 2021 Antioxidants (Basel)) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Publication | {{Publication | ||
|title=Hidalgo-Gutiérrez A, González-García P, Díaz-Casado ME, Barriocanal-Casado E, López-Herrador S, Quinzii CM, López LC (2021) Metabolic targets of coenzyme Q10 in mitochondria. Antioxidants (Basel) 10:520. doi | |title=Hidalgo-Gutiérrez A, González-García P, Díaz-Casado ME, Barriocanal-Casado E, López-Herrador S, Quinzii CM, López LC (2021) Metabolic targets of coenzyme Q10 in mitochondria. Antioxidants (Basel) 10:520. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10040520 | ||
|info=[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33810539/ PMID: 33810539 Open Access] | |info=[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33810539/ PMID: 33810539 Open Access] | ||
|authors=Hidalgo-Gutierrez A, Gonzalez-Garcia P, Diaz-Casado ME, Barriocanal-Casado E, Lopez-Herrador S, Quinzii CM, Lopez LC | |authors=Hidalgo-Gutierrez A, Gonzalez-Garcia P, Diaz-Casado ME, Barriocanal-Casado E, Lopez-Herrador S, Quinzii CM, Lopez LC | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|editor=Gnaiger E | |editor=Gnaiger E | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File:Hidalgo-Gutierrez CORRECTION.png|right|400px]] | |||
{{Template:Correction FADH2 and S-pathway}} | |||
{{Labeling | {{Labeling | ||
|enzymes=Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase | |enzymes=Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 07:29, 24 April 2023
| Hidalgo-Gutiérrez A, González-García P, Díaz-Casado ME, Barriocanal-Casado E, López-Herrador S, Quinzii CM, López LC (2021) Metabolic targets of coenzyme Q10 in mitochondria. Antioxidants (Basel) 10:520. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10040520 |
Hidalgo-Gutierrez A, Gonzalez-Garcia P, Diaz-Casado ME, Barriocanal-Casado E, Lopez-Herrador S, Quinzii CM, Lopez LC (2021) Antioxidants (Basel)
Abstract: Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is classically viewed as an important endogenous antioxidant and key component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. For this second function, CoQ molecules seem to be dynamically segmented in a pool attached and engulfed by the super-complexes I + III, and a free pool available for complex II or any other mitochondrial enzyme that uses CoQ as a cofactor. This CoQ-free pool is, therefore, used by enzymes that link the mitochondrial respiratory chain to other pathways, such as the pyrimidine de novo biosynthesis, fatty acid β-oxidation and amino acid catabolism, glycine metabolism, proline, glyoxylate and arginine metabolism, and sulfide oxidation metabolism. Some of these mitochondrial pathways are also connected to metabolic pathways in other compartments of the cell and, consequently, CoQ could indirectly modulate metabolic pathways located outside the mitochondria. Thus, we review the most relevant findings in all these metabolic functions of CoQ and their relations with the pathomechanisms of some metabolic diseases, highlighting some future perspectives and potential therapeutic implications.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
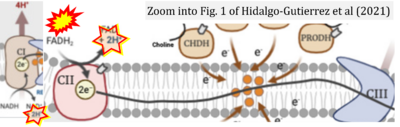
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Labels:
Enzyme: Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase