Difference between revisions of "SUIT-003 O2 ce D009"
From Bioblast
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
::: '''[[Categories of SUIT protocols |SUIT-catg]]:''' CCP | ::: '''[[Categories of SUIT protocols |SUIT-catg]]:''' CCP | ||
::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' linear [[coupling control protocol]] (CCP) | ::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' linear [[coupling control protocol]] (CCP) | ||
::: '''[[Mark names in DatLab]]:''' | ::: '''[[Mark names in DatLab]]:''' CCP_02 | ||
::: '''[[DatLab-Excel templates |DatLab-Excel template]]:''' [[Media:SUIT MiPNet08.09 CellRespiration.xlsx| | ::: '''[[DatLab-Excel templates |DatLab-Excel template]]:''' [[Media:SUIT MiPNet08.09 CellRespiration.xlsx|CCP_02.xlsx]] | ||
[[File:CCP R-L-E-ROX.jpg|left|150px]] | [[File:CCP R-L-E-ROX.jpg|left|150px]] | ||
:::* The CCP diagram may present the respiratory states (left) as an alternative to presenting the titration steps. | :::* The CCP diagram may present the respiratory states (left) as an alternative to presenting the titration steps. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
[[File:CCP_R 1Omy 2U 3Rot 4Ama.jpg|right|200px]] | [[File:CCP_R 1Omy 2U 3Rot 4Ama.jpg|right|200px]] | ||
== | == CCP_02a == | ||
:::* CCP_R 1Omy 2U 3Rot 4Ama | :::* CCP_R 1Omy 2U 3Rot 4Ama | ||
:::* '''Rot and Ama''' | :::* '''Rot and Ama''' | ||
:::: In this CCP, ROX is measured after stepwise titration of [[rotenone]] (3Rot) and [[antimycin A]] (4Ama). In many intact cells ROX measured after titration of rotenone (3Rot) is not or only slightly further inhibited by subsequent titration of animycin A (4Ama). | :::: In this CCP, ROX is measured after stepwise titration of [[rotenone]] (3Rot) and [[antimycin A]] (4Ama). In many intact cells ROX measured after titration of rotenone (3Rot) is not or only slightly further inhibited by subsequent titration of animycin A (4Ama). | ||
[[File:Huetter 2004 Biochem J.jpg|left|300px|CCP intact cells (fibroblasts)]] | [[File:Huetter 2004 Biochem J.jpg|left|300px|CCP intact cells (fibroblasts)]] | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 3 September 2016
Description
Abbreviation: CCP_R 1Omy 2U
Reference: MiPNet08.09 CellRespiration, Huetter 2004 Biochem J
MitoPedia concepts:
SUIT protocol
- SUIT-catg: CCP
- SUIT protocol pattern: linear coupling control protocol (CCP)
- Mark names in DatLab: CCP_02
- DatLab-Excel template: CCP_02.xlsx
- The CCP diagram may present the respiratory states (left) as an alternative to presenting the titration steps.
- Rot and Ama
- In this CCP, ROX is measured after titration of rotenone, antimycin A, or both in a single step. Validity of using rotenone only for inducing ROX in intact cells is evaluated by stepwise measurement of ROX after titration of rotenone (3Rot) followed by titration of animycin A (4Ama).
CCP_02a
- CCP_R 1Omy 2U 3Rot 4Ama
- Rot and Ama
- In this CCP, ROX is measured after stepwise titration of rotenone (3Rot) and antimycin A (4Ama). In many intact cells ROX measured after titration of rotenone (3Rot) is not or only slightly further inhibited by subsequent titration of animycin A (4Ama).
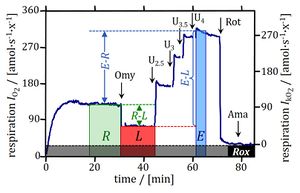
- Respiration in senescent human primary fibroblasts (0.2×106 cells/ml). Arrows show steps in the titration regime of the coupling control protocol, inducing the following respiratory states: ROUTINE (R; routine state in cell-culture medium); LEAK (L; inhibition of ATPsynthase by 1 μg/ml oligomycin); ETS (E; maximal stimulation by uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation in four subsequent titrations of the uncoupler, U, FCCP (2.5–4 μM final concentration); ROX (rotenone, Rot, and antimycin A; residual oxygen consumption). Modified after Huetter_2004_Biochem J.
- Hütter E, Renner K, Pfister G, Stöckl P, Jansen-Dürr P, Gnaiger E (2004) Senescence-associated changes in respiration and oxidative phosphorylation in primary human fibroblasts. Biochem J 380:919-28. - »Bioblast link«