|
|
| Line 29: |
Line 29: |
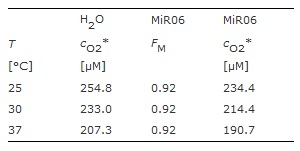
| [[Image:MiPNet06.03_Table.jpg|centre|frame|<sup>c</sup>O2* is the oxygen concentration at thermodynamic equilibrium with air under standard conditions of 100 kPa barometric pressure. ''F''<sub>M</sub> has been determined for MiR05 at 30 °C and 37 °C, and is assumed to be identical at 25 °C.]] | | [[Image:MiPNet06.03_Table.jpg|centre|frame|<sup>c</sup>O2* is the oxygen concentration at thermodynamic equilibrium with air under standard conditions of 100 kPa barometric pressure. ''F''<sub>M</sub> has been determined for MiR05 at 30 °C and 37 °C, and is assumed to be identical at 25 °C.]] |
|
| |
|
| == O2 sensor test ==
| |
| {{Technical support integrated}}
| |
| {{#set:Technical service=O2 sensor|Technical service=POS connector|Technical service=O2 signal|Technical service=Main unit|Technical service=Performance test}}
| |
| '''The O<sub>2</sub> sensor test is described as an [[OroboPOS]]''' standard operating procedure: »Bioblast pdf (on top of page).
| |
|
| |
| '''When should an O2-sensor test be performed?'''
| |
| * After switching on the O2k, every day: air calibration and stirrer test.
| |
| * Zero oxygen calibration: from time to time over weeks; bracketing zero oxygen calibrations when working at low oxygen.
| |
| * After application of a new membrane and O2-sensor service: In some cases, the signal of the OroboPOS improves (higher signal stability, less noise, shorter response time), when the O2k remains switched on over night (O2k-Chambers filled with 70% EtOH).
| |
| * During troubleshooting, particularly when [[switching components]] between the two chambers, a quick sensor test is performed after each step (stirrer test, sensor signal).
| |
|
| |
| == Air calibration in the O2k ==
| |
| {{Technical support integrated}}
| |
| '''Air calibration''' of the polarographic oxygen sensor is performed routinely on any day before an experiment. Switch on the O2k, select the experimental temperature and gain setting (Oxygraph control window [F7]). Clean the chamber and add experimental medium (at least 2.1 ml for a 2 ml chamber). Then the stopper is fully inserted while the stirrer is on, and excess medium is siphoned off the receptacle of the stopper. Now the stopper is [[Open chamber|partially opened]] and positioned with the [[Stopper-Spacer]].
| |
|
| |
| Then the stirred aqeous phase is equilibrated with the oxygen contained in the small air space included in the chamber. Use [[Graph layout]] "01 Calibration Exp. Gr3-Temp" or "02 Background Experiment".
| |
|
| |
| After stability is obtained within 20-30 min (the [[uncorrected slope]] is close to zero (less than +/- 1 pmol.s<sup>-1</sup>.ml<sup>-1</sup>), a mark is set on the blue trace of the oxygen signal (R1), and inserted in the calibration window [F5].
| |
|
| |
| Perform the oxygen calibration [F5] on-line, such that the calibration parameters are carried over automatically as a default calibration in subsequently opened DatLab files.
| |
|
| |
| Calibration parameters are copied to clipboard, for insertion into the Excel Template "[[O2k-Calibration-List]].xls". This template can be copied from [http://www.oroboros.at/index.php?o2k-o2calibration www.oroboros.at].
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| == Air calibration for high O2 experiments ==
| |
| {{Technical support integrated}}
| |
| Question: For an experiment with with high (above atmospheric levels) O2 concentrations I have to change the gain and therefore to perform a new "air calibration". How to do this?
| |
|
| |
| Answer: The [[air calibration]] has always to be done at atmospheric saturation (a point of known O2 conc.) at the final [[Gain (O2_channel)|Gain]] used in the experiment.
| |
| # Set the gain to 1.
| |
| # Perform air calibration at atmospheric saturation, [[Open chamber|open chamber]], near zero O2 slope, as usually.
| |
| # Close the chamber.
| |
| # Wait until you observe a stable [[flux at closed chamber near to air saturation]] of 2 to 4 pmol/s ml (quality control for biological contamination).
| |
| # Increase the O2 concentration either with a gas phase method or (in [[MiR06]]) with H2O2 injections.
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| == OroboPOS technical support ==
| |
| {{Technical support integrated}}
| |
| If a [[Stirrer test]] shows a slow response of the sensor, see more details in [[Slow responding sensor]].
| |
|
| |
| As the heart of the OROBOROS O2k the OroboPOS is the prime suspect when technical problems are encountered. However, frequently problems can be traced either to inadequate software settings or to other hardware components, such as the [[POS connector (technical service) |POS connector]]). Therefore, it is important to [[Locating a problem |locate the problem]], primarily with a sensor test.
| |
|
| |
| === OroboPOS technical support pages ===
| |
| {{#ask: mainlabel=Title|[[Technical service::O2 sensor||O2 signal ]]| ?Technical service}}
| |
|
| |
| === Problems that require a full sensor test to locate the problem ===
| |
| * Unstable O2 signal.
| |
| * Unstable O2 flux.
| |
| * High O2 signal at air saturation.
| |
| * High O2 signal at zero oxygen.
| |
|
| |
| === Special cases: no further localization necessary ===
| |
| * [[Slow responding sensor]], if observed in a [[Stirrer test]]. Note: The stirrer test is part of the sensor test. It is therefore recommended to do a full [[Sensor test]] whenever problems are encountered.
| |
|
| |
| === General trouble shooting procedure for the OroboPOS ===
| |
|
| |
| Confirm the problem by doing a [[Sensor test]] in the absence of biological material.
| |
|
| |
| ==== Case 1.A: No problem was visible in the [[Sensor test]] ====
| |
| Check the following DatLab settings:
| |
| * [[Gain (O2 channel)]]
| |
| * [[POS calibration]]
| |
| * Scaling
| |
|
| |
| If the problem is not visible when observing the [[Raw signal]] but is visible when observing the calibrated oxygen signal, then there is probably a problem with the [[POS calibration]].
| |
|
| |
| ==== Case 1.B: The problem was visible in the [[Sensor test]] ====
| |
| * Proceed to [[ Locating a problem|Locate the Problem]] and continue as shown below.
| |
|
| |
| ==== Case 2.A: The problem could be localized on the [[OroboPOS]] ====
| |
| '''Solutions''': Follow the instructions for oxygen sensor service [[MiPNet08.04]]. Apply [[contact oil]] to the gold pin and thread connecting the [[OroboPOS]] and [[sensor connector]]. After a sensor service or after applying a new membrane, repeating the [[sensor test]]. In some cases the O2k may be left running over night to achieve a stable signal, as seen by a repeated [[sensor test]].
| |
| If all service precautions fail to solve the problem, the [[OroboPOS]] has to be sent to OROBOROS INSTRUMENTS for further service (a recovery cannot be guaranteed), or a new sensor is applied.
| |
|
| |
| ==== Case 2.B: The problem was not located on the [[POS]] ====
| |
| '''Solutions''': If the problem was localized on an other component follow the instructions for this component. If you could not locate the problem, contact OROBOROS INSTRUMENTS.
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| == Response time of the POS ==
| |
| {{Technical support integrated}}
| |
| {{#set:Technical service=O2 sensor|Technical service=O2 signal}}
| |
| The response time of the [[Polarographic oxygen sensor]] is assessed in the [[Stirrer test]] that is part of a full [[Sensor test]]. A quantitative interpretation of the stirrer test will yield the time constant of the sensor. Such a quantitative calculation is indeed necessary for kinetic work. However, to access the suitability of a sensor for standard steady state work each user will soon gain the necessary experience to judge the outcome of a stirrer test.
| |
| :>> Example: Download [http://www.oroboros.at/index.php?id=sensor_test here].
| |
|
| |
| For how to improve the response time of a POS, see
| |
| [[Slow responding sensor]].
| |
|
| |
| The response time of the sensor is just one of several factors determining the [[time resolution]].
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| == Stirrer test ==
| |
| {{Technical support integrated}}
| |
| {{#set:Technical service=O2 sensor|Technical service=O2 signal|Technical service=Performance test}}
| |
| The [[response time of the POS]] can be most conveniently checked by a stirrer test, see
| |
| [[MiPNet06.03_POS-Calibration-SOP]], section 3.
| |
| The stirrer test is part of the [[Sensor test]] and of our proposed quality checks before every experiment described in the link above. see If the results of a stirrer test are not satisfactory the procedures suggested for a [[Slow responding sensor]] should be followed. DatLab supports an automatically controlled stirrer test [F9].
| |
|
| |
| Background information:
| |
| After switching off the stirrer the electrolyte reservoir will quickly be depleted of oxygen by the oxygen consumption of the sensor. Oxygen can only reach the sensor now in a unstirred diffusion process, therefore a new and lower equilibrium O2 concentration is established in the vicinity of the sensor. After switching the stirrer on again the O2 concentration near the sensor is quickly brought back to the same level as elsewhere in the chamber, however the sensor takes some time to respond to this change. Thus the response time of the sensor can be determined. A stirrer tests does not influence the O2 concentration in the entire chamber. A stirrer test can not be at a chamber oxygen concentration of zero (or near zero) because no change in the O2 signal will result.
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| == Cleaning the OroboPOS-Connector ==
| |
| {{Technical support integrated}}
| |
| {{#set: Technical service=POS connector|Technical service=O2 signal}}
| |
| :» '''O2k-Manual''': [[MiPNet19.18B POS-Service |»POS-Service«]].
| |
| The two electronic connections of the POS connector (to the [[POS]] and to the [[Main unit]]) make a POS connector that has been disconnected from the [[POS]] or from the [[Main unit]] or from both particularly sensitive to damage by [[ESD]]. '''It is therefore of primary importance to follow the guidelines for ESD protection [[MiPNet14.1]] whenever handling a POS connector.'''
| |
|
| |
| === Cleaning the electrical connection ===
| |
| Unscrew the [[POS]] from the [[OroboPOS-Connector]] and check both sides of the electrical connection (the gold pin and thread both on the POS and on the [[POS connector (technical service)|POS connector)]]. Remove any contamination such as grease and moisture with a fine paper towel. Soak a paper towel in ethanol and clean the gold pin and threads. If the gold pin and thread on the POS connector are discolored or stained repeat cleaning with a paper towel soaked in ethanol: Continue cleaning until a fresh paper towel stays clean. Finally, apply a drop of [[contact oil]] to each of the golden pins and threads on POS connector and POS. (You can find a small of bottle of contact oil in your accessories box). If you have also done a [[Sensor service]] or changed the POS membranes allow the oxygraph to run over night before repeating the Sensor test. If all service precautions fail to solve the problem, a new POS connector has to be applied.
| |
|
| |
| === Cleaning the spring mechanism ===
| |
| :» [[OroboPOS-Connector]]
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| == Oxygen signal and OroboPOS-Connector ==
| |
| {{Technical support integrated}}
| |
| Many problems associated with the signal from the [[POS]] may be caused by the POS connectors, e.g.
| |
| * unstable O2 signal;
| |
| * unstable O2 flux;
| |
| * high O2 signal at air saturation;
| |
| * high O2 signal at zero oxygen.
| |
|
| |
| === Troubleshooting ===
| |
| First consult in detail the
| |
| :» '''O2k-Manual''': [[MiPNet19.18B POS-Service |»POS-Service]]
| |
| :» '''O2k-SOP''': Polarographic oxygen sensors: calibration, accuracy and quality control SOP. [[MiPNet06.03 POS-Calibration-SOP |»Bioblast link«]]
| |
|
| |
| If no no problem was visible in the [[Sensor test]] check the following [[DatLab]] settings:
| |
| * [[Gain (O2 channel)]]
| |
| * [[POS calibration]]
| |
| * Scaling
| |
|
| |
| If the problem is not visible when observing the [[Raw signal]] but is visible when observing the calibrated oxygen signal, then there is probable a problem with the [[POS calibration]].
| |
|
| |
| If the problem was visible in the [[sensor test]]:
| |
| * Proceed to [[ Locating a problem|Locate the Problem ]]
| |
| * If thereby the problem was confirmed to be caused the OroboPOS-Connector: Follow the instructions for cleaning and applying [[contact oil]] as described in the sensor service manual [http://www.oroboros.at/index.php?id=o2k-pos-service [MiPNet08.04]] and in more detail at [[Cleaning the POS connector]]. If you have also done a [[Sensor service]] or changed the [[POS membranes]] allow the oxygraph to run over night before repeating the [[Sensor test]]. If all service precautions fail to solve the problem, or a new POS connector has to be applied.
| |
| * If the problem was localized on an other component follow the instructions for this component. If you could not locate the problem contact OROBOROS INSTRUMENTS.
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| == References == | | == References == |
| * [http://www.oroboros.at/?O2k-o2calibration O2k-Manual: Oxygen and pX (pH) calibration. MiPNet12.08] | | * [http://www.oroboros.at/?O2k-o2calibration O2k-Manual: Oxygen and pX (pH) calibration. MiPNet12.08] |