Description
Specific quantities are obtained when the extensive quantity is divided by system size, in contrast to intensive quantities. The adjective specific before the name of an extensive quantity is often used to mean divided by mass (Cohen et al 2008). A mass-specific quantity (e.g., mass-specific flux is flow divided by mass of the system) is independent of the extent of non-interacting homogenous subsystems. If mass-specific oxygen flux is constant and independent of system size (expressed as mass), then there is no interaction between the subsystems. The well-established scaling law in respiratory physiology reveals a strong interaction of oxygen consumption and body mass by the fact that mass-specific basal metabolic rate (oxygen flux) does not increase proportionally and linearly with body mass. Maximum mass-specific oxygen flux, VO2max, is less mass-dependent across a large range of body mass of different mammalian species (Weibel and Hoppeler 2005).
Reference: BEC 2020.1, Gnaiger_1993_Pure Appl Chem
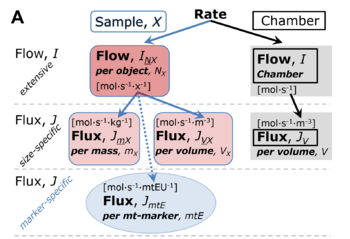
Normalization of rate. (A) Cell respiration is normalized for (1) the experimental Sample (flow per object, mass-specific flux, or cell-volume-specific flux); or (2) for the Chamber volume. Normalization yields a specific quantity flux from the extensive quantity flow. From Gnaiger 2019 MitoFit Preprints.
Compare
- Bioblast links: Normalization - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Quantities for normalization
- » Count in contrast to Number
- » Mitochondrial marker
- » O2k-Protocols: mitochondrial and marker-enzymes
- » Citrate synthase activity
- Quantities for normalization
- General
- Related keyword lists
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
Ergodynamics
Labels:
HRR: Theory