- high-resolution terminology - matching measurements at high-resolution
International System of Units
Description
The International System of Units (SI) is the modern form of the metric system of units for use in all aspects of life, including international trade, manufacturing, security, health and safety, protection of the environment, and in the basic science that underpins all of these. The system of quantities underlying the SI and the equations relating them are based on the present description of nature and are familiar to all scientists, technologists and engineers.
The definition of the SI units is established in terms of a set of seven defining constants. The complete system of units can be derived from the fixed values of these defining constants, expressed in the units of the SI. These seven defining constants are the most fundamental feature of the definition of the entire system of units. These particular constants were chosen after having been identified as being the best choice, taking into account the previous definition of the SI, which was based on seven base units, and progress in science (p. 125).
Abbreviation: SI
Reference: Bureau International des Poids et Mesures 2019 The International System of Units (SI), Gnaiger MitoFit Preprints 2020.4
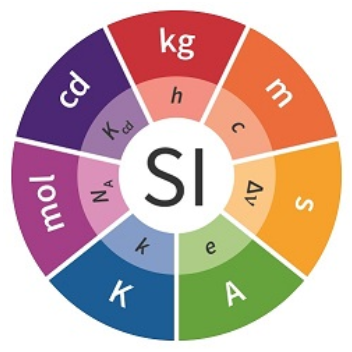
SI base quantities / SI base units
- » time / [second]
- » length / [meter]
- » mass / [kilogram]
- » electric current / [ampere]
- » thermodynamic temperature / [kelvin]
- » amount of substance / [mole]
- » luminous intensity / [candela]
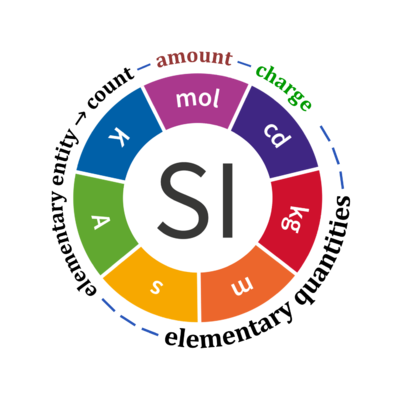
Quantity Symbol for quantity Q Symbol for dimension Name of abstract unit uQ Symbol for unit uQ [*] elementary entity *,$ UX U elementary unit x count *,$ NX = N·UX X elementary unit x amount of substance *,§ nX = NX·NA-1 N mole mol charge *,€ Qel = zX·e·NX I·T coulomb C = A·s length l L meter m mass m M kilogram kg time t T second s electric current I I ampere A thermodynamic temperature T Θ kelvin K luminous intensity Iv J candela cd
- [*] SI units, except for the canonical 'elementary unit' [x]. The following footnotes are canonical comments, related to iconic symbols.
- * For the elementary quantities NX, nX, and Qel, the entity-type X of the elementary entity UX has to be specified in the text and indicated by a subscript: nO2; Nce; Qel.
- $ Count NX equals the number of elementary entities UX. In the SI, the quantity 'count' is explicitly considered as an exception: "Each of the seven base quantities used in the SI is regarded as having its own dimension. .. All other quantities, with the exception of counts, are derived quantities" (Bureau International des Poids et Mesures 2019 The International System of Units (SI)). An elementary entity UX is a material unit, it is not a count (UX is not a number of UX). NX has the dimension X of a count and UX has the dimension U of an elementary entity; both quantities have the same abstract unit, the 'elementary unit' [x].
- § Amount nX is an elementary quantity, converting the elementary unit [x] into the SI base unit mole [mol] using the Avogadro constant NA.
- € Charge is a derived SI quantity. Charge is an elementary quantity, converting the elementary unit [x] into coulombs [C] using the elementary charge e, or converting moles [mol] into coulombs [C] using the Faraday constant F. zX is the charge number per elementary entity UX, which is a constant for any defined elementary entity UX. Qel = zX·F·nX
Fundamental relationships
References
| Bioblast link | Reference | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Brown 2018 Metrologia | Brown RJC (2018) The evolution of chemical metrology: distinguishing between amount of substance and counting quantities, now and in the future. Metrologia 55:L25. https://doi.org/10.1088/1681-7575/aaace8 | 2018 |
| Brown 2021 Metrologia | Brown RJC (2021) A metrological approach to quantities that are counted and the unit one. Metrologia 58:035014. https://doi.org/10.1088/1681-7575/abf7a4 | 2021 |
| Bureau International des Poids et Mesures 2019 The International System of Units (SI) | Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (2019) The International System of Units (SI). 9th edition:117-216. ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0 | 2019 |
| Cohen 2008 IUPAC Green Book | Cohen ER, Cvitas T, Frey JG, Holmström B, Kuchitsu K, Marquardt R, Mills I, Pavese F, Quack M, Stohner J, Strauss HL, Takami M, Thor HL (2008) Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry. IUPAC Green Book 3rd Edition, 2nd Printing, IUPAC & RSC Publishing, Cambridge. | 2008 |
| Cooper 2012 Synthese | Cooper G, Humphry SM (2012) The ontological distinction between units and entities. Synthese 187:393–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-010-9832-1 | 2012 |
| Giaquinto 2015 Oxford Univ Press | Giaquinto M (2015) Philosophy of number. In Kadosh RC, Dowker A (ed) The Oxford handbook of numerical cognition. Oxford Univ Press:17-32. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199642342.013.039 | 2015 |
| Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways | Gnaiger E (2020) Mitochondrial pathways and respiratory control. An introduction to OXPHOS analysis. 5th ed. Bioenerg Commun 2020.2. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0002 | 2020 |
| Gnaiger 2020 MitoFit x | Gnaiger E (2021) The elementary unit — canonical reviewer's comments on: Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (2019) The International System of Units (SI) 9th ed. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:200004.v2 | 2021 |
| BEC 2020.1 doi10.26124bec2020-0001.v1 | Gnaiger E et al ― MitoEAGLE Task Group (2020) Mitochondrial physiology. Bioenerg Commun 2020.1. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0001.v1 | 2020 |
| Goebel 2019 Wiley-VCH | Göbel EO, Siegner U (2019) The new international system of units (SI). Quantum metrology and quantum standards. Wiley-VCH 249 pp. | 2019 |
| Hofstadter 1979 Harvester Press | Hofstadter DR (1979) Gödel, Escher, Bach: An eternal golden braid. A metaphorical fugue on minds and machines in the spirit of Lewis Carroll. Harvester Press:499 pp. | 1979 |
| Kadosh 2015 Oxford Univ Press | Kadosh Roi Cohen, Dowker Ann, ed (2015) The Oxford handbook of numerical cognition. Oxford Univ Press:1185 pp. | 2015 |
| Kahneman 2011 Penguin Books | Kahneman D (2011) Thinking, fast and slow. Penguin Books 499 pp. | 2011 |
| Wilkie 2015 Front Psychol | Wilkie James EB, Bodenhausen Galen V (2015) The numerology of gender: gendered perceptions of even and odd numbers. Front Psychol 6:810. | 2015 |
- Bioblast links: SI base units - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Entity, count, and number, and SI base quantities / SI base units
Quantity name Symbol Unit name Symbol Comment elementary UX elementary unit [x] UX, UB; [x] not in SI count NX elementary unit [x] NX, NB; [x] not in SI number N - dimensionless = NX·UX-1 amount of substance nB mole [mol] nX, nB electric current I ampere [A] A = C·s-1 time t second [s] length l meter [m] SI: metre mass m kilogram [kg] thermodynamic temperature T kelvin [K] luminous intensity IV candela [cd]
- Fundamental relationships
- » Avogadro constant NA
- » Boltzmann constant k
- » elementary charge e
- » Faraday constant F
- » gas constant R
- » electrochemical constant f
- Fundamental relationships
- SI and related concepts
MitoPedia concepts:
Ergodynamics