Description
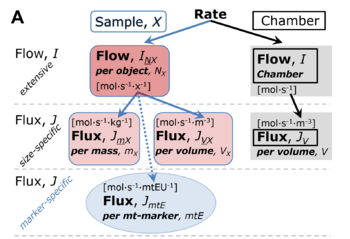
Flux, J, is a specific quantity. Flux is flow, I [MU·s-1 per system] (an extensive quantity), divided by system size. Flux (e.g., oxygen flux) may be volume-specific (flow per volume [MU·s-1·L-1]), mass-specific (flow per mass [MU·s-1·kg-1]), or marker-specific (e.g. flow per mtEU). The motive unit [MU] of chemical flow or flux is the advancement of reaction [mol] in the chemical format.
Abbreviation: J
Reference: BEC 2020.1, Gnaiger 1993 Pure Appl Chem
Normalization of rate. (A) Oxygen flow is normalized for (1) the experimental Sample (flow per object, mass-specific flux, or cell-volume-specific flux); or (2) for the Chamber volume. Normalization yields a specific quantity flux from the extensive quantity flow. From Gnaiger 2019 MitoFit Preprints.
References
| Bioblast link | Reference | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Gnaiger 1993 Hypoxia | Gnaiger E (1993) Efficiency and power strategies under hypoxia. Is low efficiency at high glycolytic ATP production a paradox? In: Surviving hypoxia: Mechanisms of control and adaptation. Hochachka PW, Lutz PL, Sick T, Rosenthal M, Van den Thillart G (eds) CRC Press, Boca Raton, Ann Arbor, London, Tokyo:77-109. | 1993 |
| Gnaiger 1993 Pure Appl Chem | Gnaiger E (1993) Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of energy transformations. Pure Appl Chem 65:1983-2002. http://dx.doi.org/10.1351/pac199365091983 | 1993 |
| Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways | Gnaiger E (2020) Mitochondrial pathways and respiratory control. An introduction to OXPHOS analysis. 5th ed. Bioenerg Commun 2020.2. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0002 | 2020 |
| BEC 2020.1 doi10.26124bec2020-0001.v1 | Gnaiger E et al ― MitoEAGLE Task Group (2020) Mitochondrial physiology. Bioenerg Commun 2020.1. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0001.v1 | 2020 |
- Bioblast links: Normalization - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Quantities for normalization
- » Count in contrast to Number
- » Mitochondrial marker
- » O2k-Protocols: mitochondrial and marker-enzymes
- » Citrate synthase activity
- Quantities for normalization
- General
- Related keyword lists
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
Ergodynamics
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry