Tang 2014 Front Physiol
| Tang X, Luo YX, Chen HZ, Liu DP (2014) Mitochondria, endothelial cell function, and vascular diseases. Front Physiol 5:175. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00175 |
Tang X, Luo YX, Chen HZ, Liu DP (2014) Front Physiol
Abstract: Mitochondria are perhaps the most sophisticated and dynamic responsive sensing systems in eukaryotic cells. The role of mitochondria goes beyond their capacity to create molecular fuel and includes the generation of reactive oxygen species, the regulation of calcium, and the activation of cell death. In endothelial cells, mitochondria have a profound impact on cellular function under both healthy and diseased conditions. In this review, we summarize the basic functions of mitochondria in endothelial cells and discuss the roles of mitochondria in endothelial dysfunction and vascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, diabetic vascular dysfunction, pulmonary artery hypertension, and hypertension. Finally, the potential therapeutic strategies to improve mitochondrial function in endothelial cells and vascular diseases are also discussed, with a focus on mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants and calorie restriction.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
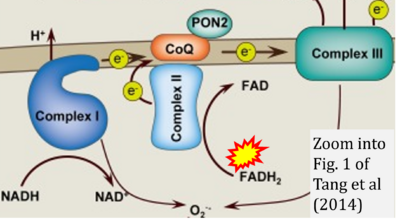
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Labels:
Enzyme: Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase